Set-up the E-Maj access policy
A bad usage of E-Maj can break the database integrity. So it is advisable to only authorise its use to specific skilled users.
E-Maj roles
To use E-Maj, it is possible to log on as superuser. But for safety reasons, it is preferable to take advantage of both roles created by the installation script:
emaj_adm is used as the administration role ; it can execute all functions and access to all E-Maj tables, with reading and writing rights ; emaj_adm is the owner of all log objects (schemas, tables, sequences, functions),
emaj_viewer is used for read only purpose ; it can only execute statistics functions and can only read E-Maj tables.
All rights given to emaj_viewer are also given to emaj_adm.
When created, these roles have no connection capability (no defined password and NOLOGIN option). It is recommended NOT to give them any connection capability. Instead, it is sufficient to give the rights they own to other roles, with GRANT SQL verbs.
Giving E-Maj rights
Once logged on as superuser in order to have the sufficient rights, execute one of the following commands to give a role all rights associated to one of both emaj_adm or emaj_viewer roles:
GRANT emaj_adm TO <my.emaj.administrator.role>;
GRANT emaj_viewer TO <my.emaj.viewer.role>;
Of course, emaj_adm or emaj_viewer rights can be given to several roles.
Giving rights on application tables and objects
It is not necessary to grant any privilege on application tables and sequences to emaj_adm and emaj_viewer. The functions that need to access these objects are executed with the extension installation role, i.e. a superuser role.
Synthesis
The following schema represents the recommended rights organisation for an E-Maj administrator.
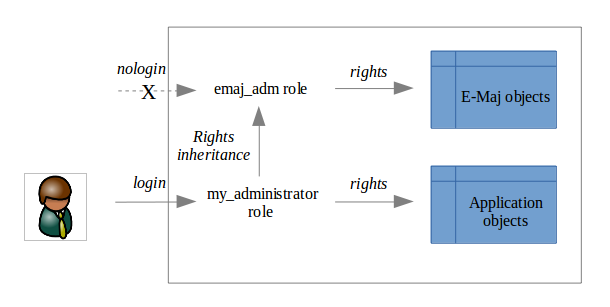
Of course the schema also applies to emaj_viewer role.
Except when explicitly noticed, the operations presented later can be indifferently executed by a superuser or by a role belonging to the emaj_adm group.